Since 2000, our company has been producing 4A11 aluminum piston skirt forgings of certain diesel engines, and the product quality is stable. However, in 2014, our company has a number of piston skirt parts. After rough machining, a large number of spots on the surface of the parts were found. In order to determine the defect properties, the quality of the piston skirt forgings was further improved, and the repeated occurrence of the defects was avoided. the study.
1. Test process and results
A serious piston skirt was taken from 10 parts of the surface graying, and the samples were taken from the serious visual defects, and the chemical composition analysis, hardness test, low magnification observation and analysis were performed on the defect parts.
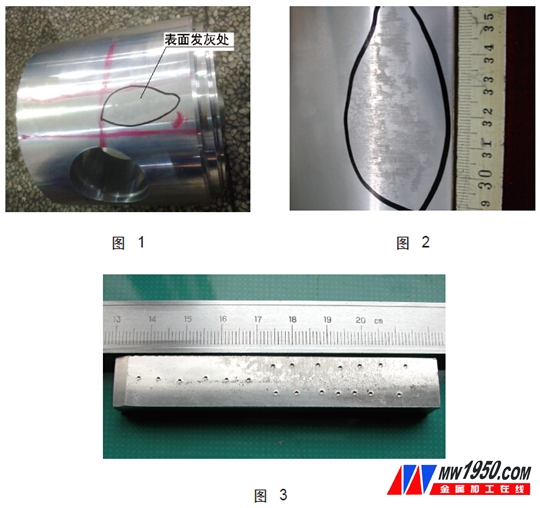
(1) Analysis of macroscopic defects of forgings The macroscopic photographs of the defects are observed (see Fig. 1 and Fig. 2). It can be seen from Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 that there are some color gray areas on the surface of the piston, which are significantly different from other normal parts. .

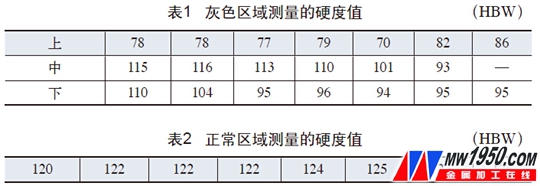
(2) Hardness analysis Due to the large defect area, we measured the hardness of multiple points in the gray area of ​​the forging (see Figure 3), and measured them from the top, bottom, and bottom.
The test results are shown in Table 1. From the hardness value measured in the gray area of ​​Table 1, and the hardness value measured in the normal area of ​​Table 2, it can be seen that the hardness of the gray defect portion is significantly lower than that of the normal portion.
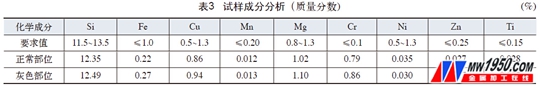
(3) Component analysis The composition analysis of the gray defect part and the normal part sample is shown in Table 3. As can be seen from Table 3, there is almost no difference in chemical composition, which meets the requirements of GB/T3090.
(4) Low-fold defect rating The surface and longitudinal sections of the gray defect area were subjected to low-pickling inspection according to the GB/T3246 standard, and the grain size was evaluated (see Fig. 4 and Fig. 5).
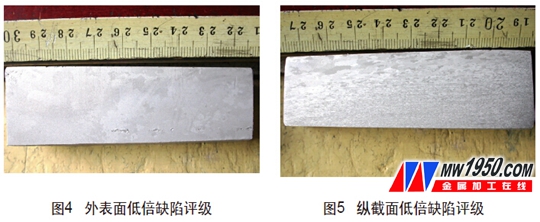
Through the outer surface low-magnification test and the grain size class determination standard GB/T3246, the local grain size is 7 grade, determined by the longitudinal section low-fold test and the grain size class determination standard GB/T3246. Degree 7 grade, the coarse crystal belt is deepest than 10mm.
2. Defect discussion analysis
(1) The gray part of the gray defect is due to the large difference in grain size between the grain and the matrix, and the coarseness of the grain causes the hardness to decrease.
(2) Formation mechanism of coarse crystal defects The mechanism of coarse crystal generation: the free energy of the metal after plastic deformation is increased, the structure is in an unstable state, and when it is heated to an appropriate temperature, the crystal nucleus is re-formed and grown. If the heating temperature is favorable for grain growth or heating and holding time is too long, the grains will grow to form coarse grains. There are two types of grain growth, one is gradually growing up, and the relative size between the crystal grains is relatively close; the other is abnormal growth, which shows that the relative size between the crystal grains is extremely different. The grain grows very large. In the coarse grain defects of aluminum alloy die forgings, the probability of abnormal grain growth is large.
(3) Analysis of coarse crystal defects The coarse crystal defects of aluminum alloy die forgings are related to the material of forgings, forging process parameters, forging shape, mold temperature, heat treatment process parameters, mold surface roughness and other factors.
(4) Analysis and investigation Through the analysis of people, machine, material, method, ring and test, except for personnel changes, the rest have not changed, that is, 5t die forging hammer, 4A11 piston skirt blank, piston skirt forging, heat treatment process parameters The ambient temperature and detection methods have not changed.
This batch of parts was produced for the newly formed team members, and the forging method of the material 4A11 piston skirt was not mastered. The 5t die forging hammer is an impact load type equipment, the stroke is not fixed, and the deformation speed of the forging blank is difficult to control, thus requiring a higher level of the operator. For the forging of 4A11 piston skirt, when the deformation speed of the forging blank is faster, the aluminum alloy is less than recrystallized, and the recrystallized core is less, and the forging after forging is easy to form coarse crystal. Therefore, we analyze that the initial hammering force of the die forging is large, resulting in an excessive deformation of the aluminum piston skirt forgings, and the intense flow of metal is the root cause of the coarse grain on the surface of the aluminum piston skirt. In response to this problem, we added operational guidance in the process: the die forging requires a light strike to gradually transition to a heavy blow, and finally a heavy blow 1 to 3 times.
After taking the above measures, we trial-produced 10 pieces. As a result, after the 10 pieces of blanks were processed, none of the surfaces were grayed.
3. Conclusion
(1) The speckle on the surface of the 4A11 forging piston is caused by coarse grains, and the appearance is different in color from the base portion.
(2) Controlling the deformation speed during forging can improve the surface quality of the piston.
About the author: Nanfen Ni, Shaanxi Diesel Heavy Industry Co., Ltd.
Solar Panels,275W Solar Panels,260W Poly Solar Panels,Full Power Mono Solar Panels
ZHONGWEI CITY YINYANG NEW ENERGY , https://www.yinyangnewenergy.com