In the face of the increasing trend of the proportion of intermittent renewable energy in the power system, what impact will the traditional hydropower generating units that undertake the burden of grid regulation have, and how to deal with it? Recently, Nature Communications ("Nature · Communication") published online research progress on this issue by Professor Yang Jiandong of the College of Water Resources and Hydropower.
The thesis is titled Burden on hydropower units for short-term balancing of renewable power systems ("Short-term regulation burden of hydropower units in renewable energy power systems"). The research was completed by the team of Professor Yang Jiandong in collaboration with the relevant teams of Uppsala University in Sweden, Vattenfall of the Swedish National Power Company, and Oak Ridge National Laboratory in the United States. The first signed unit of the paper is Wuhan University, and the first author and corresponding author are associate researchers Yang Weijia.
At present, how to deal with the intermittent power generation of renewable energy such as wind energy and solar energy, and efficiently solve the problem of grid connection and consumption of renewable energy power is a hotspot in the field of global energy research. Hydropower units have the advantages of fast load regulation rate and large regulation range. Many studies have shown that reasonable hydropower regulation will be the key to ensuring the safe and stable operation of power systems with high proportion of renewable energy. However, what impact will the increasing burden of grid regulation have on hydropower units? The mechanism of component wear and loss of power generation efficiency under frequent frequency regulation of hydropower units is not yet clear, and the corresponding power market compensation mechanism needs to be further studied. In addition, the research on optimal dispatching and economic operation of generating units is usually carried out from the medium and long-term level, and the research on small time scale (second level) is rarely reported.
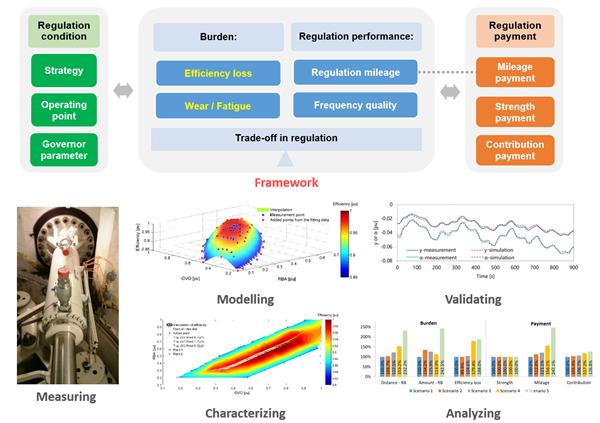
This research aims at the two aspects of the trade-off between the burden of hydropower generating units in the primary frequency regulation of the power grid and the regulation performance. Based on the second-level time scale, a quantitative evaluation framework (Framework) combining the technical characteristics and economic indicators of the power station is proposed. This study takes efficiency loss, component wear, adjustment mileage, and frequency quality as the four core indicators during the frequency modulation process of the unit, and establishes a mathematical model of a hydraulic-mechanical-electrical coupling hydraulic power generation system with an axial-flow rotary double-adjusting turbine. Various operating conditions of the unit and the "burden reduction" operation strategy were evaluated.
Based on the adjustment and compensation mechanism of the relevant generating units in China, Switzerland, and the United States, this study expands and comparatively analyzes three different frequency modulation economic compensation methods, including Mileage, Strength, and Contribution. The researchers used this framework and model to explore the evolution of the frequency regulation burden and economic compensation of hydropower generating units in scenarios of high power fluctuation, low inertia, and weak damping in future renewable energy power systems.
The framework and model proposed in this study can be used as an effective analysis tool for power generation companies to obtain favorable unit operation strategies to reduce losses and increase compensation benefits, and can be used by power grid companies and transmission system operators to deeply analyze the actual adjustment performance and Compensate the relationship between incentive mechanisms. At the end of the paper, it was also mentioned that it is hoped that hydropower regulation research will attract wider attention from all walks of life and the participation of more people to provide guarantee for the efficient operation of renewable energy power systems. (Correspondent Chen Huan)
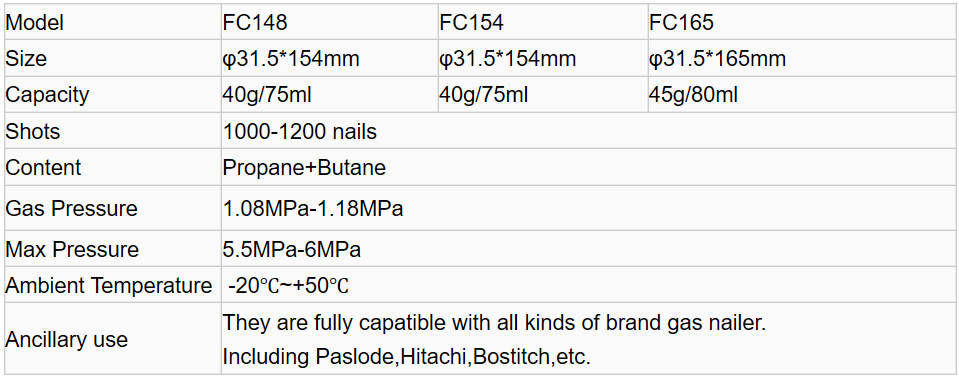
FC165 Gas Can for Gas Nailer Gas Fuel Cell ,Gas Fuel Cell for Gas Powered Construction Tools
Specifications:
Model NO.: FC165
Size: Ø31.5*165mm (1.24" x 6.50"
Content :Propane + Butane
Pressure :16 ~ 18bar
Net Weight :40g/80ml (1.41Oz)
Shots Qty :1,200 shots (approx.)
Certificate:
CE

Applications
- Fastening with GCN40,GCN40SP,GFN3490,GCN40L,GI200 and other most famous models of framing gun.
Heheng Technology Gas Fuel Cell FC165
Gas Fuel Cell,Gas Can For Gas Gun Nailer,Propane And Butane Fuel Cell,Gas Fuel Cell,Gas Fuel Cell for Gas Powered Construction Tools
Yibin Heheng Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.chinadirectfastening.com