9013 is an NPN type low power transistor. The transistor, which is one of the basic semiconductor components, has a current amplification function and is a core component of the electronic circuit. The triode is to make two closely spaced PN junctions on a semiconductor substrate. The two PN junctions divide the whole semiconductor into three parts. The middle part is the base area and the two sides are the emitter area and the collector area. There are two types of transistor arrangements: PNP and NPN. S9013 NPN transistor main purposes: as audio amplification and radio 1W push-pull output and switches. Below we introduce 9013 triode pin parameters, non-9014, 9013 series triode pin identification methods to help you to further understand the 9013 triode .
(A) 9013 triode model comparison
S9014, s9013, s9015, s9012, s9018 series of crystal low-power transistors, the display text plane toward himself, from left to right for the e emitter b base c collector; for small and medium-power plastic triode according to map its plane For yourself, with three pins facing downwards, ebc, s8050, 8550, and C2078 are the same from left to right. Use the following pin diagram (pin diagram):
Transistor pinout
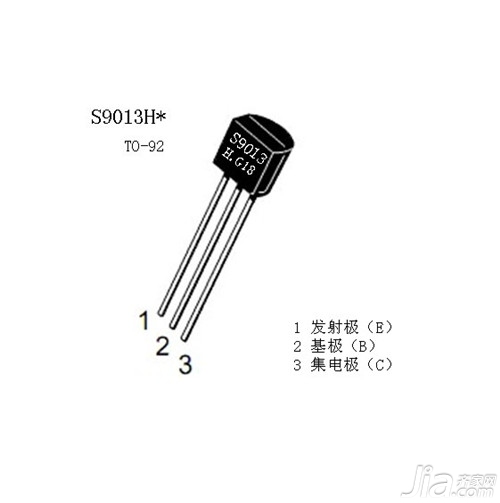
At present, there are many types of crystal transistors in the country, and the arrangement of the pins is different. In the use of transistors with indeterminate pin arrays, measurements must be taken to determine the correct position of each pin (the three poles of the triode should be measured with a multimeter below. The method), or find the transistor manual, clarify the characteristics of the transistor and the corresponding technical parameters and data.
Non-9014,9013 series triode pin identification method:
(a) Determine the base. Use a multimeter R×100 or R×1k to measure the forward and reverse resistance values ​​between each of the three electrodes of the tube. When the first table pen is used to pen a certain electrode, and the second table pen is in contact with the other two electrodes, the low resistance is measured. Then the electrode to which the first pen is connected is the base b. At this time, pay attention to the polarity of the multimeter pen, if the red pen is connected to the base b. When the black pens are respectively connected to the other two poles, the measured resistance is small, then the tested pipe can be judged as a PNP type triode; if the black pen is connected to the base b, the red pens are in contact with the other two poles, respectively. With a small resistance, the triode to be tested is an NPN tube such as 9013, 9014, 9018.
(b) Judging triode collector c and emitter e. (Using a PNP transistor as an example) Place the multimeter in an R×100 or R×1K block, the base b of the red meter, and when using a black pen to contact the other two pins respectively, the two measured resistance values ​​will be one. Larger, smaller. In a small resistance measurement, the black probe leads to the collector; in a large resistance measurement, the black probe leads to the emitter.
Do not disassemble the triode to judge its good or bad
In practical applications, low-power triodes are directly soldered on the printed circuit board. Due to the high mounting density of the components, the disassembly is more troublesome. Therefore, the voltage of each pin of the tested pipe is often measured by the DC voltage of the multimeter when detecting. The value is used to infer whether it is working properly and determine the quality of the transistor.
If 9013, like 9014, NPN uses the multimeter to check their pin, the black pen is connected to one pole, and the red pen is connected to the other two poles. When both poles have 5K resistance, the black pen is connected to the B pole. At this time, use the black and red pens to connect the other two poles together and add them together with the tip of the tongue (In fact, you can use the tongue to moisten your fingers and touch them with your fingers, which is not hygienic anyway). The black pens are connected to the pole and B poles. The black meter with a small resistance is connected to the C pole. (The above is measured by the pointer table. The digital table is the reverse of the positive and negative levels of the red pen digital multimeter.)

(B) 9013 transistor pin parameters
Parameter: Structure NPN
Collector-emitter voltage 25V
Collector - base voltage 45V
Emitter-base voltage 0.7V
Collector current Ic Max 0.5A
Dissipation power 0.625W
Working temperature -55°C ~ +150°C
Characteristic frequency 150MHz
Magnification D64-91 E78-122 F96-135 G122-166 H144-220 I190-300
The main purpose of the amplifier circuit.
Editor's summary: The above is the 9013 triode pin parameters, non-9014, 9013 series triode pin identification methods related to the introduction, hope to help meet the needs of friends! For more information, please continue to follow our website. You can also purchase more of your favorite products on Qijia Mall!
multimeter
Solenoid valves are electromechanical devices that are used to control the flow of fluids or gases in a variety of applications. They are classified based on their function, construction, and application.
Based on Function:
1. Normally Closed (NC) Solenoid Valve: In this type of valve, the valve is closed when there is no power supply to the solenoid coil. The valve opens when the coil is energized.
2. Normally Open (NO) Solenoid Valve: In this type of valve, the valve is open when there is no power supply to the solenoid coil. The valve closes when the coil is energized.
3. Direct Acting Solenoid Valve: In this type of valve, the solenoid coil directly controls the valve stem, which opens or closes the valve.
4. Pilot Operated Solenoid Valve: In this type of valve, the solenoid coil controls a pilot valve, which in turn controls the main valve.
Based on Construction:
1. Brass Solenoid Valve: These valves are made of brass and are used in applications where the fluid or gas is not corrosive.
2. Stainless Steel Solenoid Valve: These valves are made of stainless steel and are used in applications where the fluid or gas is corrosive.
3. Plastic Solenoid Valve: These valves are made of plastic and are used in applications where the fluid or gas is not corrosive and the valve is not subjected to high pressure.
Based on Application:
1. Solenoid Water Valve: These valves are used in applications where water is the fluid being controlled.
2. Solenoid Air Valve: These valves are used in applications where gas is the fluid being controlled.
3. Steam Solenoid Valve: These valves are used in applications where steam is the fluid being controlled.
4. Fuel Solenoid Valve: These valves are used in applications where fuel is the fluid being controlled.
Solenoid Valve,Mini Solenoid Air Valve,Normally Open One-Way Solenoid Air Valve,3V Electric Solenoid Air Valve
Shenzhen DYX Technology Co.,Limited , https://www.dyxpump.com