Chemicals are prone to fires and explosions. However, different chemicals and fires under different conditions have very different methods for fighting fires. If they are not handled properly, they will not only effectively extinguish the fire, but will further increase the disaster. In addition, because the chemicals themselves and their combustion products are mostly highly toxic and corrosive, they can easily cause poisoning and burns. Therefore, fighting a dangerous chemical fire is an extremely important and very dangerous job.
Persons engaged in the production, use, storage and transportation of chemicals, and firefighting and rescue personnel should be familiar with and master the main dangerous characteristics of the chemicals and their corresponding fire-fighting measures, and conduct regular fire drills to strengthen the emergency response capacity. In the event of a fire, each worker should clearly understand their roles and responsibilities, master the use of fire-fighting facilities, evacuation procedures for personnel, and special requirements for extinguishing hazardous chemicals.
1 . Fire fighting measures
(1) Initial fire fighting
1 Quickly close the upstream and downstream valves of the fire site and cut off all materials entering the fire accident site;
2 Before the fire has been expanded to uncontrollable, a mobile fire extinguisher or other various fire-fighting equipment and equipment on site shall be used to extinguish the initial fire and control the fire source.
(2) Take protective measures
In order to prevent fire from endangering adjacent facilities, the following protection measures may be taken:
1 Take timely cooling protection measures for surrounding facilities;
2Rapid evacuation of materials threatened by fire;
3 Some fires may cause the outflow of flammable liquids. Sandbags or other materials may be used to build embankments to intercept drifting liquids, or to divert ditches to direct materials to safe locations.
4 Use felt and sea grass curtains to block the wells and yin wells to prevent the spread of fire.
(3) Fire fighting
The use of fire extinguishers and fire extinguishing methods for each type of chemical must be used to safely control the fire. The fire fighting of chemical fires shall be carried out by a professional fire brigade. Other personnel shall not act blindly. After the fire brigade arrives, the material media will be introduced to fight against the fire.
2 . Basic measures to fight against compressed or liquefied gas fires.
Compressed or liquefied gas is always stored in different containers, or by pipe. The pressure of the gas stored in the smaller cylinder is high, and it is prone to burst when heated or flamed. After the gas leaks, when the fire source has formed a stable combustion, the risk of explosion or re-explosion is much smaller than when the combustible gas leaks unburned. In case of a compressed or liquefied gas fire, the following basic countermeasures should generally be taken.
(1) Extinguishing gas fires Do not blindly suppress fire extinguishing. In the absence of plugging measures, you must maintain stable combustion. Otherwise, a large amount of combustible gas leaks out and mixes with air, and it will explode in the event of a fire, and the consequences will be unthinkable.
(2) First of all, extinguish the fire of the combustible material ignited by the fire source, cut off the spread of fire, control the scope of combustion, and actively rescue the injured and trapped people.
(3) If there is a pressure vessel in the fire or a pressure vessel that is threatened by the radiant heat of the flame, the evacuation should be evacuated to the safe area under the cover of the water gun. A sufficient water gun should not be deployed to carry out cooling protection. In order to prevent the container from bursting and hurting, the personnel performing the cooling should try to use the water in a low position or use a solid shelter on the spot. For horizontal storage tanks, cooling personnel should choose the four sides of the tank as shooting positions.
(4) If the gas pipeline leaks and catches fire, try to find the gas source valve. When the valve is in good condition, the fire will automatically extinguish as soon as the gas inlet and outlet valves are closed.
(5) If the leakage of the storage tank or pipeline is invalid, the gas pressure and the size and shape of the leakage outlet should be judged according to the fire, and the corresponding plugging materials ( such as cork stoppers, rubber stoppers, airbag stoppers, adhesives, and bends) should be prepared. pipe tools, etc.).
(6) After plugging work is ready, water can be used to fight the fire, and dry powder, carbon dioxide, and halogenated alkanes can also be used to extinguish the fire. However, it is still necessary to use water to cool the burned can or wall. After the fire is extinguished, plugging with plugging material should be immediately used to block leakage, and at the same time, dilute and disperse the leaked gas with mist-like water. If it is confirmed that the leak is very large and it cannot be plugged at all, it is only necessary to cool the fire container, its surrounding containers and combustible materials, and control the fire range until the gas burns out and the fire automatically extinguishes.
(7) The on-site commander should pay close attention to all kinds of danger signs. If the flame of a container that fails to recover stable combustion or heat radiation after a long period of time when the fire is extinguished, the flame will brighten, scream, shake, etc. Make accurate judgments in due time and promptly issue retreat orders. Site personnel should quickly retreat to a safe area after seeing or hearing a predetermined retreat signal.
3 . Basic measures for fighting flammable liquids
Flammable liquids are usually stored in containers or pipelines. Different from gas, liquid containers are closed, some are open, and they are generally atmospheric. Only the pressure of the liquid in the reaction vessel ( furnace, kettle ) and transfer pipe is high. Liquids, whether they are ignited or not, will drift along the surface ( or surface ) if there is a leak or spillage. Moreover, flammable liquids have problems such as density and water solubility, whether they can be saved by water or ordinary foam, and dangers. A lot of boiling and splashing problems, so fighting a flammable liquid fire is often a difficult battle. In case of flammable liquid fires, the following basic countermeasures should generally be adopted.
(1) Firstly, we should cut off the spread of the fire, cool and evacuate the pressure threatened by the fire, sealed containers and combustibles, control the burning range, and actively rescue the injured and trapped people. If there is liquid flow, dikes should be built ( or use oil booms ) to intercept flammable liquids or trench diversions.
(2) Understand and control the name, density, water solubility of fire liquids, and the dangers of no poison, corrosion, boiling, splashing, etc. in order to take appropriate fire fighting and protective measures.
(3) For larger tanks or rogue fires, the area of ​​ignition should be accurately determined.
(4) Liquid fires in small areas ( generally less than 50m2 ) are generally extinguished by fog water. Extinguishing with foam, dry powder, carbon dioxide, and halogenated alkanes (1211 , 1301) is generally more effective.
(5) Large-area liquid fires must be selected based on their relative density, water solubility, and size of the burning area.
(6) Liquids that are lighter than water and insoluble in water ( such as gasoline, benzene, etc. ) are often ineffective when extinguished with direct water and spray water. Use ordinary protein foam or light water foam to extinguish the fire. When extinguishing with dry powder or haloalkane, the fire extinguishing effect depends on the size of the burning area and the burning conditions. It is better to cool the tank wall with water.
(7) Liquids that are heavier than water and insoluble in water ( such as carbon dioxide ) can be used to save water in the event of fire, and water can be used to extinguish the fire on the surface of the liquid. The use of foam is also effective. Dry powder and halo-alkane are used to extinguish the fire. The fire-extinguishing effect depends on the size of the combustion area and the burning conditions. It is better to cool the tank wall with water.
(8) Water-soluble liquids ( such as alcohols, ketones, etc. ) , although they can theoretically be diluted with water, use this method to make the liquid flash point disappear, the water must account for a large proportion of the solution. This requires not only a large amount of water, but also easy to make the liquid overflow, while the ordinary foam will be destroyed by the water-soluble liquid ( if the ordinary foam strength is increased, it can weaken the fire ) , so it is best to use a solvent-resistant foam to save. When extinguishing with dry powder or haloalkane, the fire extinguishing effect depends on the size of the burning area and the burning conditions. It is also necessary to cool the tank wall with water.
(9) Extinguishing a flammable liquid fire that is toxic, corrosive, or highly toxic to combustion products, the rescue personnel must wear protective masks and take protective measures.
(10) Fight liquid fires such as crude oil and heavy oil that have the risk of boiling over and splashing. If possible, use measures such as taking and releasing water and stirring to prevent the occurrence of boiling over and splashing. In the case of fire extinguishing, care must be taken to calculate that boiling over may occur. , splashing time and observing whether there are signs of boiling over, splashing. When a commander discovers a danger sign, he or she should promptly make an accurate judgment and issue a withdrawal order in a timely manner so as to avoid causing casualties and equipment losses. After the rescue personnel sees or hears the unified retreat signal, they should immediately withdraw to the safe zone.
(11) When a flammable liquid pipe or tank leaks and catches fire, while cutting off and spreading the fire to a certain extent, it shall try to find and close the inlet and outlet valves if the pipeline valve is damaged or the tank leaks. , should quickly prepare the leaking material, and then use foam, dry powder, carbon dioxide or water spray, etc. to extinguish the rogue flame on the ground to clear obstacles for plugging, then extinguish the flame of the leak, and quickly take measures to plug leaks. Different from the gas plugging, the plugging of the liquid fails once, and it can be blocked several times in a row, as long as the ground is covered with foam, and the liquid flow is blocked and the surrounding fire source is controlled, and the leaked liquid does not need to be ignited.
4 . Basic measures for fighting fires of explosives
Explosives generally have a special or temporary storage warehouse. Due to the internal structure containing explosive genes, these items are excited by external factors such as friction, impact, vibration, and high temperature, and are prone to explosions, and are even more dangerous when exposed to fire. In case of an explosive fire, the following basic measures should generally be taken.
(1) Rapidly determine and identify the possibility and danger of recurrence of explosions, and seize the favorable opportunity before the explosion and recurrence of an explosion, and take all possible measures to fully prevent the occurrence of another explosion.
(2) Do not cover with sand, so as not to increase the explosive power of explosives.
(3) If there is a possibility of evacuation, and under the condition that personal safety is reliable, it shall immediately organize the force to evacuate the explosives around the fire area to form a barrier around the fire area.
(4) During the stacking of explosives, the water stream should be lifted to prevent the strong water from directly hitting the stack, so as to prevent the stack from collapsing and causing another explosion.
(5) Fire extinguishers should make full use of the ready-made shelters on the site or use as low as possible shots in prone position to take self-protection measures as much as possible. Fire vehicles should not stop at water sources too close to explosives.
(6) When a fire extinguisher finds that there is a danger of a re-explosion, it shall immediately report to the site. The on-site command shall immediately make an accurate judgment, and if there is any sign or danger of another explosion, the retreat order shall be issued immediately. After the firefighting personnel sees or hears the retreat signal, they should quickly withdraw to the safety zone. When the firefighters have no time to retreat, they should lie down on the spot.
5 . The basic countermeasures for fighting fires with wet flammable materials
Wet and flammable articles can react chemically with moisture and water, generate combustible gases and heat, and sometimes even if there is no open flame, they can automatically catch fire or explode, such as metal potassium, sodium and triethylaluminum ( liquid ) . Therefore, when there is a certain amount of such articles, it is absolutely forbidden to use water, foam, and acid-alkali fire extinguishers and other fire extinguishing agents to save. This particularity of this type of object has brought great difficulties to its fire suppression.
Under normal circumstances, wet flammable items due to their fire extinguishing measures in the event of fire in the storage time required separate storage or isolation piled up separately stored, but in practice it is sometimes difficult to completely complete, especially in production and It is even more difficult to do in the transportation process. For example, aluminum products often have aluminum powder everywhere. For wet flammable articles with strong packaging, tight sealing, and small quantities, the storage requirements allow the same room to be separated or stored in the same cabinet. This has brought greater difficulties to their fire fighting work. Firefighters should be careful in fighting. The following basic countermeasures are generally taken for fires in contact with wet flammable materials.
(1) First of all, it should be clear about the name and quantity of wet flammable items, whether it is mixed with other items, the scope of combustion, and the spread of fire.
(2) If there is only a small amount ( usually within 50g ) of wet flammable items, it can be saved with a large amount of water or foam, regardless of whether it is mixed with other items. When water or foam just touches the fire point, it may increase the fire in a short time, but when a small amount of wet flammable articles burns out, the fire will soon extinguish or decrease.
(3) If there are a large number of wet flammable items and there is no coexistence with other items, it is absolutely forbidden to use water or foam, acid and alkali and other wet extinguishing agents to save. In the case of wet flammable materials, dry powder, carbon dioxide, and halogenated alkanes are used to save. Only metallic potassium, sodium, aluminum, magnesium, and other individual items use carbon dioxide and halogenated alkanes. Solid and wet flammable materials are covered with cement, dry sand, dry powder, diatomaceous earth and vermiculite. Cement is an extinguishing agent that is relatively easy to obtain when it comes to fighting solid fires when wet. For dust in wet flammable materials such as magnesium powder, aluminum powder, etc., do not spray pressurized extinguishing agent to prevent the dust from blowing up and form an explosive mixture with air and cause an explosion.
(4) If there are more wet flammable items mixed with other items, it should first find out what kind of items are on fire and whether the packaging of wet flammable items is damaged. A small quantity of water can be used to test the water gun first by switching the water gun to the fire point. If there is no obvious increase in the fire, it proves that the wet product has not caught fire and the packaging has not been damaged. Immediately use a large amount of water or foam to save the fire. Extend wet flammable materials that have been exposed to water or still in wet areas to safe areas. If the fire is significantly increased after the test of the water, it is proved that the wet flammable items have caught fire or the packaging has been damaged. Water, foam, and acid-alkali fire extinguishers should be prohibited. If the liquid is used dry powder and other fire extinguishing agents to save; if the solid application of cement, dry sand and other coverage; in case of potassium, sodium, aluminum, magnesium light metal fire, it is best to use graphite powder, sodium chloride and special light metal fire extinguishing agent.
(5) If other items of fire threaten adjacent wet and flammable items, use tarpaulins or plastic tarps to cover the wet flammable items, and then cover the quilts. Sheung Shui. If the site of wet flammable materials is not too high, a waterproof dike may be built around it. When water or foam is used to fight a fire, there should be a certain amount of force monitoring on adjacent wet flammable items.
Due to the special properties of wet flammable materials, which cannot be saved by commonly used water and foam fire extinguishing agents, personnel and firefighters engaged in the production, operation, storage, transportation and use of such items should understand and be familiar with their name and main hazard characteristics in peacetime. .
6 . Basic countermeasures for fighting fires of poisons and corrosives
Toxic and corrosive products have some damage to the human body. The poisonous products cause poisoning of the human body mainly through oral or inhalation of human vapor or through skin contact. Corrosion products cause chemical burns to the body through skin contact. Some poisons and corrosives can catch fire on their own, and some do not ignite on their own, but can catch fire when they come in contact with other combustibles. The following basic countermeasures should generally be taken for fires of such items.
(1) Firefighters must wear protective clothing and wear protective masks. Under normal circumstances, full body protection can be used. Special protective clothing should be used for fires with special requirements. Taking into account the limitations of the scope of filter-type gas mask anti-virus, in the fight against poison fires should use isolated oxygen mask or air mask. In order to properly use and adapt to the fire, strict adaptive training should be conducted in peacetime.
(2) Actively rescue injured and trapped people and limit the scope of combustion. The fires of poisons and corrosive products can easily cause casualties. After the fire-fighting personnel take protective measures, they should immediately invest in finding and rescuing the work of injured and trapped persons, and work hard to limit the scope of combustion.
(3) When fighting, use low-pressure water or spray water to avoid corrosion and poisonous products spilling. In the case of acid or alkali corrosion products, it is best to administer the corresponding neutralizing agent for dilution and neutralization.
(4) Leakage of poisonous and corrosive product containers should be taken after the extinguishing of fire. Corrosion products need to be plugged with anti-corrosion materials.
(5) Concentrated sulphuric acid will release a lot of heat when it encounters water, which will lead to boiling and splashing. Special attention must be paid to protection. When fighting the fire in contact with concentrated sulfuric acid and other flammable materials, when the amount of concentrated sulfuric acid is small, a large amount of low-pressure water can be used to quickly save the fire. If the amount of concentrated sulfuric acid is large, use carbon dioxide, dry powder, halogenated alkanes, etc. to extinguish the fire, and then separate the fired items from the concentrated sulfuric acid.
7 . Basic measures for fighting flammable solids and flammable materials
Combustible solids and flammable materials are generally rescued by water or foam. Compared with other types of chemical dangerous goods, they are easier to fight, so long as they control the burning range, they can be extinguished gradually. But a few flammable solids, spontaneous combustion Extinguishing special articles, such as 2, 4 - dinitrophenyl ether, dinitro naphthalene, naphthalene, phosphorus and the like.
(1) 2 , 4 -Dinitroanisole, dinitronaphthalene, naphthalene, etc. are flammable solids capable of sublimation and emit flammable vapors upon heating. In case of fire, spray water and foam can be used to save fire and cut off the spread of fire. However, it should be noted that fire extinguishing cannot be assumed to have completed the fire extinguishing work because the flammable vapors sublimated after being heated can be unknowingly floating in the upper air The formation of explosive mixtures, especially in the interior, is prone to deflagration. Therefore, the fire of such items must not be confused by the illusion. During the extinguishing process, misty water should be sprayed over and around the burning area from time to time, and all fire sources in and around the burning area should be extinguished with water.
(2) Yellow phosphorus is an auto-ignition product that has a very low auto ignition point and can rapidly oxidize and warm up in air and self-ignite. In the event of a yellow phosphorus fire, it is first necessary to cut off the spread of fire and control the scope of combustion. For the yellow phosphorus on fire, apply low pressure water or spray water to save. The impact of high-pressure DC water can cause yellow phosphorus splashes, leading to an increase in disasters. When the yellow phosphorus molten liquid flows, it is intercepted by mud, sandbags and other embankments and cooled with mist-like water. The phosphorus blocks and solidified yellow phosphorus after cooling are clamped into water storage containers using forceps. If it is too late to clamp, it can be covered with sand, but it should be marked. After the fire is extinguished, it is gradually concentrated in the water container.
(3) A small number of flammable solids and pyrophoric articles shall not be used to save water and foam. For example, phosphorus trisulfide, aluminum powder, aluminum alkyl, and insurance powder shall be treated separately according to specific conditions. Dry sand and dry powder without pressure injection should be used. Save.
8 . Basic countermeasures for fighting fires from radioactive materials
Radioactive objects are special items that emit alpha, beta, gamma rays, and neutron fluxes that are invisible to humans but that can seriously damage human life and health. In order to fight fires of such items, special measures must be taken to protect against radiation. Normal production, operation, storage and transportation, as well as the use of such items of units and fire departments, should be equipped with a certain amount of protective equipment and radioactive test equipment. The following basic countermeasures should generally be taken in the event of a fire in such items.
(1) Firstly send the lean personnel to carry the radioactive test equipment and test the radiation ( agent ) quantity and range. Testers should take protective measures as much as possible.
1 In areas where the amount of radiation ( agent ) exceeds 0.0387 C / kg , a written warning sign stating "life-threatening, no entry" should be provided.
2 In the area where the amount of radiation ( agent ) is less than 0.0387C / kg , a warning sign with "Danger of Radiation and Do Not Approach" should be set. Testers should also conduct uninterrupted tour monitoring.
(2) In areas where the radiation ( agent ) volume is greater than 0.0387C / kg , the fire extinguishing personnel cannot penetrate the source deep enough to extinguish the attack. In areas where the amount of radiation ( agent ) is less than 0.0387C / kg , extinguishments can be quickly performed or foam, carbon dioxide, dry powder, and halogenated alkanes can be used to rescue and rescue the injured.
(3) For radioactive materials that have not been damaged in the field packaging of the fire, protective equipment may be worn under the cover of the water gun to manage evacuation. If it cannot be evacuated, cooling protection should be performed on the spot to prevent new damage and increase the amount of radiation ( agent ) . The damaged container should not be moved or impacted with water to prevent the expansion of radioactive contamination.
Carbon Steel Press fittings pipeline system is widely used in hot water supply, fire protection.
Compared with traditional pipeline system, it`s not only more economical, safer and healthier,
but also easier and faster for installation with longer service life.

1. Carbon Steel Press Fittings range:
Coupling -- Equal coupling, Reducing coupling, Slip coupling, coupling with male/ female threads;
Elbow -- Equal elbow, Elbow 90°, Elbow 45°, Reducing elbow, Elbow with plain end, Elbow with wall plate, and Elbow with male/ female threads;
Tee -- Equal tee, Reducing tee, Tee with wall plate, and Tee with male/ female threads;
Others-- Pipe cap, Pipe Bridge and Flange connector.
2. Material: Galvanized carbon steel, 1.0034C-Stahl,Kohlenstoffstahl, ACCIAIO AL CARBONIO.
3. Size: 3/8``-4``inch or as request, pipe wall thickness: 1.0--2.0mm
Sizes range:
DVGW W534:1995: 15, 18, 22, 28, 35, 42, 54, 76.1, 88.9, 108mm.
JIS G 3448-1980: 15.88, 22.22, 28.58, 34.00, 42.7, 48.6, 76.1, 88.9, 108mm.
4. Standard:
Press fitting standard: (DIN) DVGW W534-1995; (JIS) JWWA G116:2001; GB/T 19228.1-2003
Pipe standard: DIN10312:2003; GB/T 19228.2-2003
O-ring sealing standard: CEN EN 681-1:2006; GBT 19228.3-2003
5. O-Ring Seal: "Chlorinated butyl rubber" (CIIR), EPDM, HNBR, NBR and FKM, etc.
EPDM (black): max working pressure 16bar, working temperature from -20℃ to 120℃, Suit medium: cold and hot water, compressed Air etc.
6. Galvanization: all carbon steel pipe fittings are plated with rust-resistant zinc.
7. Anneal: all stainless steel pipe fittings are annealed in inert gases before packing.
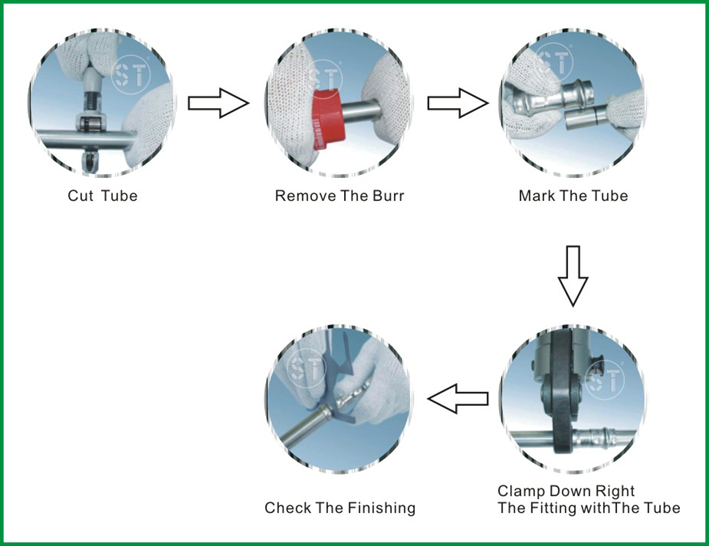
Installation and Connection Order
Equipments And Quality Control
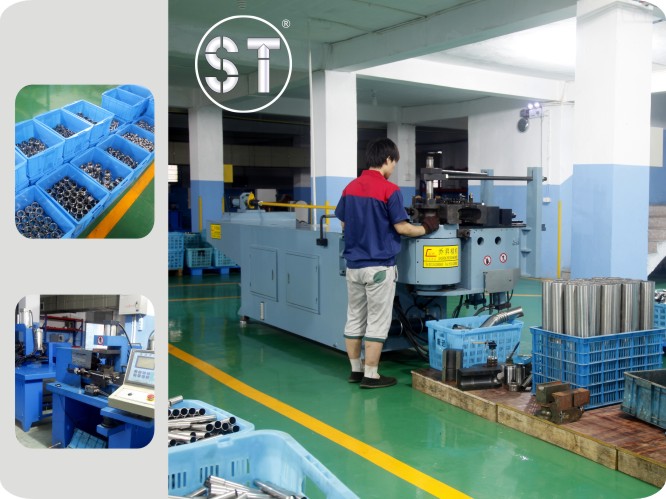

Orderly Workshop
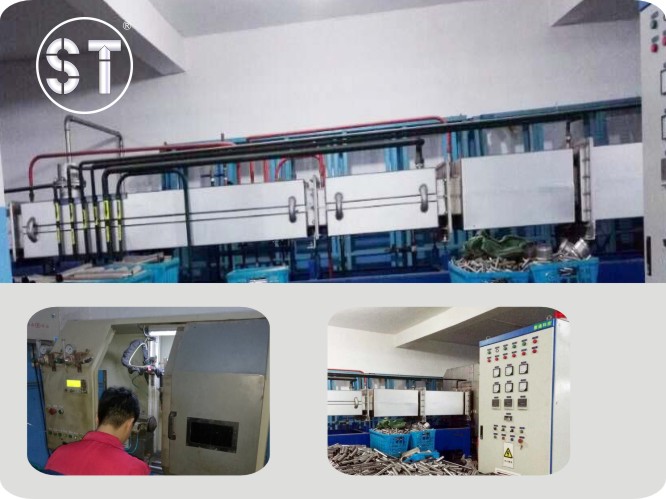

Efficient Anneal Equipment
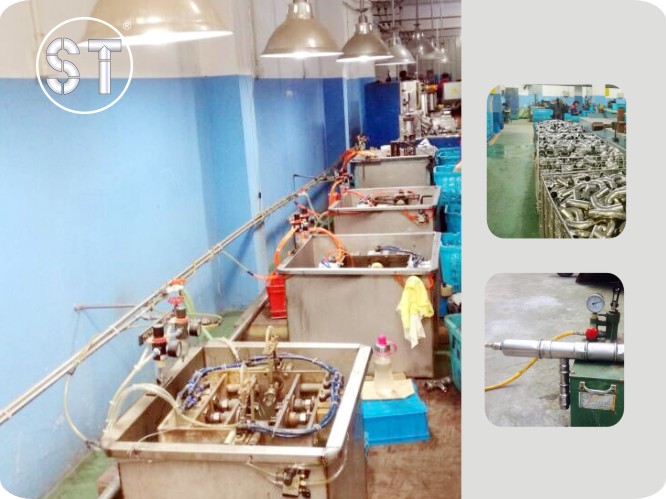

Pressure Testing
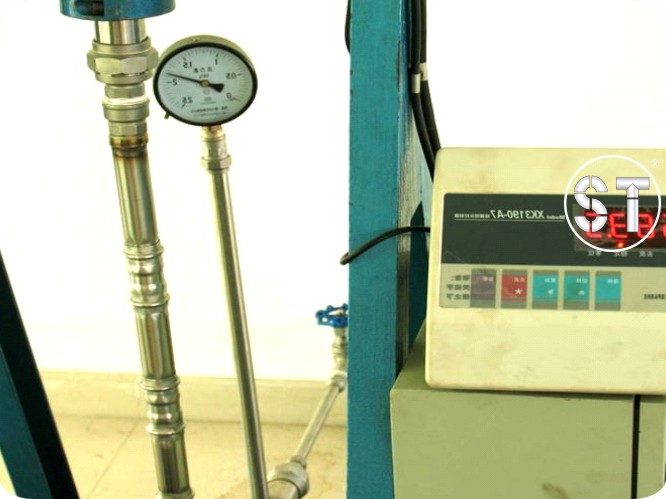

Tensile Testing
Carbon Steel M Profile Press Fittings(DVGW)
Carbon Steel M Profile Press Fittings,Carbon Steel Press Fittings,Steel Press Elbow Extension Fitting,M Profile Carbon Tee
WENZHOU KASIN VALVE PIPE FITTING CO., LTD. , https://www.kasinvalvefitting.com