1 anti-rust phosphating process
The early application of the phosphating process is anti-rust, and the steel parts are phosphatized to form a layer of phosphate film, which acts as a rust preventive. The rust-preventing period of the phosphating anti-rust treatment can reach several months or even several years (for oil-coated workpieces), and is widely used for rust prevention and rust-proof phosphating during process, transportation, packaging, storage and use. There are three major varieties of iron phosphating, zinc phosphating and manganese phosphating.
The iron-based phosphating main bath component is a ferrous phosphate solution, does not contain an oxidizing accelerator, and has a high free acidity. The iron phosphating temperature is higher than 95 ° C, the treatment time is longer than 30 min, the phosphating film is more than 10 g / m 2 , and has the dual functions of derusting and phosphating. This high-temperature iron phosphating is currently used in applications because the phosphating rate is too slow.
Manganese phosphating has the best performance as rust-proof phosphating. The microstructure of phosphating film is densely packed and is the most widely used rust-proof phosphating. Adding or not adding a promoter can increase the rate of phosphating film formation if nitrate or nitroguanidine promoter is added. The treatment temperature is usually 80 to 100 ° C, the treatment time is 10 to 20 minutes, and the membrane weight is 7.5 g/m 2 or more. Zinc phosphating is also a widely used rust-proof phosphating. Nitrate is usually used as a promoter. The treatment temperature is 80-90 ° C, the treatment time is 10-15 min, the phosphating film is more than 7.5 g/m 2 , and the phosphating film is microscopic. The structure is generally a compact pile of needles.

General process of rust-proof phosphating:
Degreasing and descaling - water cleaning - surface conditioning activation - phosphating - water cleaning - chromate treatment - drying - grease or dye treatment
The workpiece treated by the strong alkali strong acid will cause the phosphating film to coarsen, and the surface adjustment activation can refine the crystal grains. Zinc phosphating can be adjusted by oxalic acid and colloidal titanium. Manganese phosphating can be activated by insoluble manganese phosphate suspension. Iron phosphating generally does not require adjustment of the activation process. The phosphating workpiece can be greatly improved in rust resistance by chromate sealing. For example, after varnishing or dyeing treatment, the rust resistance can be improved by several or even several tens, as shown in Table 1.
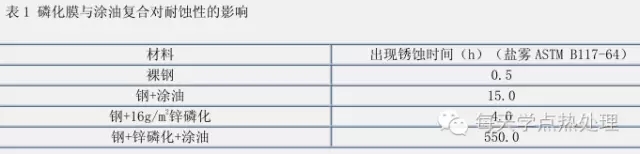
Excerpted from Freeman D B. Phosphating and Metal Pretreatment Woodhead-Faukner, 1986.
2 wear-resistant anti-friction lubrication phosphating process
For the engine piston ring, gear, refrigeration compressor and other types of workpieces, it not only bears a load, but also sports friction, requiring the workpiece to reduce friction and wear. The manganese-based phosphating film has high hardness and thermal stability and is resistant to abrasion, and the phosphating film has a good anti-friction lubrication effect. Therefore, it is widely used in piston rings, bearing bearings, compressors and other components. The wear-resistant antifriction phosphating treatment temperature is 70-100 ° C, the treatment time is 10-20 min, and the phosphating film is more than 7.5 g/m 2 .
In the cold processing industry, such as: take-up, drawing, extrusion, deep drawing and other processes, the phosphating film is required to provide friction-reducing lubrication performance, generally using zinc-based phosphating. First, the zinc-based phosphating film is saponified to form a good lubricity. Zinc stearate layer, the second is zinc phosphating operation temperature is relatively low, can be phosphating at 40, 60 or 90 ° C, phosphating time 4 ~ 10min, sometimes even tens of seconds, phosphating The film weight requirement is ≥3g/m2.
The process flow is:
Wear-resisting anti-friction phosphating anti-friction lubrication phosphating (cold processing)
Degreasing, derusting, degreasing, descaling, cleaning, cleaning, cleaning
Manganese phosphating phosphating
Water washing water cleaning
Dry saponification (sodium stearate)
Apply grease to dry
3 Pre-paint phosphating process
The phosphating treatment before the primer is applied will improve the adhesion of the paint film to the base metal, improve the corrosion resistance of the entire coating system, and provide protection between processes to avoid secondary rust. Therefore, the primary problem of phosphating before lacquering is that the phosphating film must have excellent compatibility with the primer, and the rust resistance of the phosphating film itself is secondary, and the phosphating film is fine and dense, and the film is thin. When the phosphating film is thick, it will have a negative effect on the overall performance of the film. Phosphating system and process selection mainly consists of: workpiece material, oil rust degree, geometry; time interval of phosphating and painting; primer type and construction method and equipment conditions of relevant sites.
In general, low carbon steel higher carbon steel is easy to be phosphating, and phosphating film forming performance is better. For rust (oxidized scale) workpieces must be subjected to an acid washing process, and the pickled workpieces will cause a lot of troubles for phosphating, such as rust yellowing during the process, removal of residual acid solution, coarsening of the phosphate film, etc. . The pickled workpiece is generally subjected to surface conditioning treatment before zinc or zinc manganese phosphating.
In batch production, due to the limited conditions, the phosphating workpiece must be stored for a period of time before painting, so the phosphating film itself is required to have good rust resistance. If the storage period is more than 10 days, moderate temperature phosphating should be used, such as medium temperature zinc system, medium temperature zinc manganese system, medium temperature zinc calcium system, etc. The thickness of the phosphate film should be between 2.0 and 4.5 g/m2. The phosphating workpiece should be dried immediately, and it should not be naturally dried to avoid rusting at the cracks and welds. If the storage period is only 3 to 5 days, it can be phosphatized with low-temperature zinc and light iron, and the drying effect will be better than natural drying.
3.1 Single chamber spray phosphating process
The entire pre-treatment process has only one spray chamber, and there are a plurality of liquid storage tanks under the spray chamber, and different treatment liquids spray the workpiece and then flow back to the respective tank bodies. For example, first spray the degreasing liquid, after the degreasing liquid flows back to the degreasing tank, close the valve; then spray the water to wash, close the water washing valve after the water washing is completed; the next step is to spray the phosphating solution, the single chamber processing method can be implemented as follows Process flow:
Degreasing - Phosphating "two in one" (light iron) - water cleaning - (chromium closure) - delivery.
Degreasing - water cleaning - phosphating - water cleaning - (chromium closure) - delivery
Degreasing - water cleaning - surface adjustment - phosphating - water cleaning - (chromium closure) - delivery
This phosphating process generally does not advocate the arrangement of pickling processes to avoid corrosion of the equipment or corrosion between processes. The single-chamber process equipment occupies less space, is simple and easy to operate, but is wasteful, and is only suitable for batch production occasions with small batches. Another method similar to this, using a peripheral small-capacity tank body to process the liquid, pumping the liquid through the pump and the pipe, mixing with the hot water, spraying on the workpiece to achieve the degreasing and phosphating effect, and the liquid medicine is not recovered after the spraying. This method is simpler but more wasteful.
3.2 Multi-chamber “standard†station phosphating process:
1 pre-degreasing 50 ~ 70 ° C 1 ~ 2min
2 degreasing 50 ~ 70 ° C 2 ~ 4min
3 water cleaning 1 to 2 channels at room temperature 0.5 to 1.0 min
4 surface adjustment normal temperature 0.5 ~ 1.0min
5 phosphating 35 ~ 60 ° C 2 ~ 6min
6 water cleaning <2 channels at room temperature 0.5 ~ 1.0min
7 deionized water wash at room temperature 0.5 ~ 1.0min
8 chromate treatment 40 ~ 70 ° C 0.5 ~ 1.0min
9 drying below 180 ° CThe treatment method can adopt three methods: full spray, full immersion, and spray-soak combination. For the household appliance industry, the full spray method is generally adopted, which is highly efficient, and the entire pre-treatment can be completed in only ten minutes, saving the site equipment. The automotive industry is popular with a combination of spray-soak.
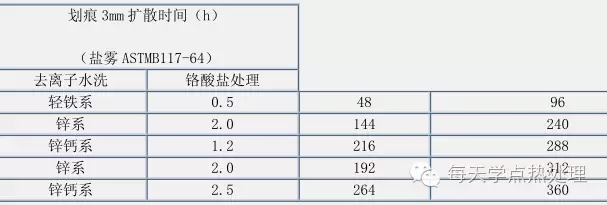
The surface adjustment process is not necessary, and the same effect can be achieved by adding a surface conditioner to the degreasing tank. Deionized water washing after phosphating is essential. Phosphate treatment after phosphating can improve the corrosion resistance of the entire coating system (see Table 2), but due to environmental pollution of chromium, it should be used with caution.
Table 2 Effect of chromate treatment on corrosion resistance of paint film
3.3 Mixing phosphating process (corroded workpiece)
1 degreasing 40 ~ 70 ° C 3 ~ 8min
2 water cleaning at room temperature 0.5 ~ 1.0min
3 pickling 40 ~ 70 ° C 3 ~ 8min
4 water cleaning at room temperature 0.5min
5 neutral and normal temperature 0.5 ~ 1.0min
6 surface adjustment at room temperature 0.5min
7 phosphating 35 ~ 60 ° C 3 ~ 10min
8 water cleaning at room temperature 0.5 ~ 1.0min
9 deionized water wash at room temperature 0.5 ~ 1.0min
10 chromate water washing 40 ~ 70 ° C 0.5 ~ 1.0min
(11) Drying <180°CUnless there are sufficient reasons, the pickling process generally does not use a spray treatment method, which causes a series of problems such as equipment corrosion and rust between workpiece processes. All other processes can be combined with full spray or spray-dip.
For the mixing parts (rust-free workpiece, rust, oxide scale workpiece mixing treatment at the same time), the method of degreasing and rusting "two-in-one" instead of step-by-step degreasing and rust removal has been applied for several decades, and the same satisfactory results can be obtained. . For pickling and degreasing and derusting, "two in one" is generally suitable for non-volatile inorganic acids.
Threaded rod, as its name suggests, is a metal rod that is threaded throughout the entire length of the rod. It's typically made from carbon, zinc coated or stainless steel. The threading allows for bolts and other types of fixings to be fastened onto the rod to suit many different construction applications.
Thread Rod,Threaded Bar,Galvanized Threaded Rod,1 Inch Threaded Rod
Hebei W.M fastener manufacturing CO.,Ltd , https://www.wmfasteners.com