In autumn and winter, the temperature is gradually decreasing, and greenhouse vegetables are also prone to various problems. It is necessary to take various measures in advance to prevent and deal with these problems, which will reduce the yield and quality of vegetables and cause a substantial reduction in production. So, what are the reasons and principles for taking these measures?
1. Why should I try to extend the lighting time?
As the saying goes, everything grows by the sun. Light is the driving force for photosynthesis of crops. Without sunlight, crops can't be photosynthesized. Without photosynthesis, crops can't grow without vegetables, food and fruits, even meat, eggs, milk, etc., we live on it. food. In theory, the longer the illumination time, the higher the photosynthesis efficiency, and the more organic products produced by the crop, that is, the higher the yield and quality. In the winter in the north, the illumination time is short, so it is necessary to extend the illumination time in the greenhouse as much as possible. When the sun comes out, quickly uncover the quilt or grasshopper, and cover it after the sun sets. Of course, considering the temperature problem, you can control it flexibly in time.
2. Why is it necessary to uncover the quilt in the snowy weather?
During the growth of plants, there is also a respiration that releases energy and carbon dioxide. It and photosynthesis are the physiological processes of two different directions of decomposition and synthesis of two substances. Photosynthesis must be carried out with light, and respiration can be done with or without illumination. That is to say, during the daytime photosynthesis, in fact, respiration is also taking place. During the snowy weather, although there is no direct sunlight, there is still scattered light. Plants can use these seemingly weak light to perform photosynthesis to maintain growth. If the quilt or grasshopper is not uncovered, there is no light in the shed, there is no photosynthesis, but only breathing. On the one hand, the nutrients stored in plants will be continuously consumed and reduced with respiration. Over time, the growth and resistance of plants are greatly reduced, the ability to resist infection by bacteria is reduced, and diseases are more susceptible; Plants have their own habit of growing to light. When there is no light or light, they grow upwards, resulting in slenderness, which is not only easy to fall but also prone to disease. Therefore, on cloudy days or when there is little snowfall, the quilts should be uncovered as much as possible during the day, and the snow covered on the shed film should be cleaned.
3. Why should greenhouse vegetables be temperature-changed?
As we all know, the temperature and change of temperature will affect the survival, growth and development of living things. The same is true for plants. Temperature affects the various physiological processes of plant endosomes, such as respiratory decomposition, photosynthetic synthesis, absorption and transport of water and nutrients, and conversion and accumulation of substances. In turn, these physiological metabolic intensities are also affected by other factors. During the day, morning, morning, noon, evening and late night, the physiological metabolism of plants is different because of the combined effects of light and temperature. The purpose of agricultural production is to make better use of these laws to allow crops to produce more quality and better agricultural products. Cultivation of vegetables in greenhouses is an agricultural production model for this purpose. Variable temperature management can purposely adjust the growth of vegetables to better achieve our production goals. In the morning, after the quilt was uncovered, the intensity and efficiency of photosynthesis gradually increased with the increase of light and temperature, reaching a peak around 13:00, and the intensity of photosynthesis decreased with light and temperature in the afternoon. The photosynthetic products produced by green organs such as leaves in the daytime reach a peak at the speed of transfer to other organs such as roots and fruits. At night, the transfer of this material gradually slows down. Before the sun comes out, the temperature in the greenhouse is minimized, and the physiological metabolism of plants Also reduced to a minimum. This is the physiological activity of the plant itself. We should make better use of these laws in production management. By covering the shed film, uncovering the quilt and releasing the wind, we can control the temperature changes in different time periods to maximize our production. purpose. For example, the cucumber in the melon period, in the morning, after the quilt is uncovered, the temperature in the shed is around 15~18 °C, and gradually rises to 30 °C. Through the control of the vent, the thermometer reading above the cucumber plant can be read at 33 °C. This has been maintained until around 13:00 noon. If the temperature rises slowly and low in the morning, it is not conducive to the photosynthesis, and the moisture in the shed is also difficult to evaporate and dissipate, resulting in high humidity, which is prone to diseases such as gray mold, black star disease, downy mildew, etc.; if the temperature rises Too fast and high, it is easy to cause symptoms of daily burning; in the afternoon, the temperature gradually drops to 28 ° C, 25 ° C, 23 ° C, the photosynthesis efficiency gradually decreases, and the photosynthetic products synthesized in the stems and leaves begin to be transferred to the fruits and roots, to After the sun sets, the quilt is covered, and the temperature in the shed is maintained at 18~20 °C. At this time, the transformation and transport of photosynthetic products in the leaves reach a peak. If the temperature is low at this time, the photosynthetic products in the leaves are difficult to transfer out, and the bubble leaf symptoms will appear. If the temperature is high, the photosynthetic products in the leaves will be transformed in situ to cause the leaves to accelerate and grow. At night, the temperature of the shed continues to decrease. Before sunrise, the temperature of the shed should be maintained above 10 °C, and 15 °C is most suitable. The night temperature is high, the respiration is strengthened, the nutrient consumption in the plant is too large, and the seedlings are weak; when the night temperature is low for a long time, the phenomenon of flower topping is prone to occur, which is also conducive to the invasion of germs.
4. Why do you advocate drip irrigation or watering under the membrane?
Watering is the most important measure in vegetable management. However, there are some specific details about when to water, water or small water, daytime pouring or evening pouring. Under the action of temperature and gravity, the moisture in the soil is always a dynamic process.
The water poured into the soil will partially sink and some will be absorbed by the plants. The water on the surface of the soil and the water absorbed by the plants will be transpiration into the air, which will increase the humidity of the air. Watering in the warm morning, after the watering is finished, sealing the air outlet and increasing the temperature of the shed will accelerate the evaporation of soil moisture, then open the air outlet, and disperse the water in the air of the shed to the outside of the shed. The air humidity at night is not It will be too big. If it is watered on a cloudy day or in the afternoon, the temperature in the shed is low, the evaporation of soil moisture is slow, and the air can not be ventilated, resulting in high air humidity, and water droplets on the surface of the leaves, stems or fruits of the vegetables at night. More, in the morning, when you uncover the quilt, you will feel beautiful when you see the crystal clear water on the leaves or on the fruit, but this beauty will cause trouble to the vegetables. Many pathogens that inhabit the soil or the air prefer water. Water is the favorite living environment for these germs. Waterborne bacteria breed faster, and it is easier to invade through the wound or directly into the plant organs, causing the disease to occur. For example, cucumber downy mildew, keratosis, gray mold, tomato leaf mold, ulcer disease, pith necrosis and other diseases occur in low temperature and cloudy days, and the indoor air humidity in the shed is severe.
This requires avoiding evaporation of water when watering. There are two specific measures, one is to look at the water, and do not water in the afternoon. Watering in the morning on a sunny day, the higher temperature in the shed will make the evaporation of soil moisture faster. With the help of air release management, the water can be discharged out of the shed in time, and the air humidity at night will not be very high. However, this is related to the amount of water and temperature level at that time, and measures need to be taken to control it.
The second measure is to pour small water and water or drip irrigation under the membrane. When the water is poured at one time, the amount of water evaporated into the air is more. Especially in the case where the temperature in the shed is not high, the time required for the transpiration of water is long, and it is inevitable that more water will condense on the vegetable organs at night. Therefore, in the production, when watering greenhouse vegetables is required in winter, the first water should be poured or drip, and the second film should be watered. This not only limits the proportion of water evaporating into the air, but also the water poured under the film is difficult to evaporate into the air, so that the humidity of the air in the booth can be better controlled, and the probability of occurrence of the disease is greatly reduced.
5. Why do you want to see the seedlings watering?
Although plants are inseparable from water, in the process of plant growth, the demand for water is sometimes more and less, and there is a certain regularity. In the process of vegetable management, measures should be taken around this rule of plants, and it is not appropriate to water them by subjectively. Under normal circumstances, on the basis of sufficient bottom, the seedling period and growth stage of vegetables require less water, and the water demand is large in the result period.
In production, it is necessary to look at the comprehensive evaluation of whether to water the vegetables. Look at the sky to see the seedlings.
Let me talk about the seedlings first. The seedling mentioned here refers to the vegetable plant, not a specific growth period. Whether it is cucumber, tomato or even vegetables such as pepper, when the water supply is too high, the growth rate is fast, the color of the leaves and stems is light or even yellowish, the internodes are long and thin, the leaves are large and thin, and the stem tips Higher than the young leaves below. Conversely, in the absence of water, the leaves are dark but dim, the stem segments are short and thick, the stem tips are lower than the height of the young leaves, and the plants are short. Of course, the specific performance is also related to the water supply level, temperature and nutrition. For example, when there is a lack of water at high temperatures, the leaves of cucumber have a focal edge, that is, the edges of the leaves are dry. Further development, the leaves are wilting at noon; when the nitrogen supply is high, the water will be more watered, the plants will have a leafy appearance, the stems are thick and long, and the flowering is less or the flowering is heavy. The soil has too much water for a long time, and when the temperature is low, the roots are red or brown, and the roots are not rooted or rotted. If the soil is in a drought for a long time, the root development will gradually shift from multiple roots to less roots and no roots.
6. Why do you want to see the ground watering?
In the current cultivation mode, crops absorb water from the soil through the root system. The soil is actually a reservoir for crop growth. Therefore, when judging whether to water the plants, you must look at the water condition of the soil. Dig a piece of soil and inspect it carefully. You will find that the soil is composed of many large and small particles with different sizes of pores. Among them are soil water and soil air. Moisture is a dynamic process in the soil. Water and water directly affect the growth of vegetables.
There is a need for a specific numerical indicator in production to measure the amount of water in the soil, ie the maximum water holding capacity in the soil field. When water is supplied to the soil, the water in the soil gradually increases. When all the pores of the soil are filled with water, the water is continuously poured, and some of the excess water will settle down to the groundwater with the attraction of the earth, or accumulate in the deep layer. , or lost to rivers and lakes and other water sources; water collected on the surface, and then transpiration into the air. After stopping the watering, excessive moisture gradually decreases downward or upward. When only the pores in the soil are filled with water, the soil water content at this time is called the maximum water holding capacity in the soil field.
For sandy loam or loam, at this time, a little force will be used to squeeze out the water, and the water content is equivalent to 100%; after a while, the water in the soil pores continues to decrease downward or upward. The surface is slightly dry. At this time, grab a handful of soil and force it into a soil mass, but squeeze it out without water, stretch out the palm of your hand, the soil mass does not spread out, put it on your chest, stretch your fingers, and the earth mass does not scatter. The soil water content is between 85 and 95%; if the soil mass is scattered, the soil water content is equivalent to 60-80%; if the soil is grasped by force, it can be agglomerated, but the fingers are spread out, The water content is less than 50%; if the soil is not tight enough to hold the soil, the water content is lower. For vegetables in the seedling stage, the soil holding capacity in the soil field is 50% or slightly lower; for the early vegetables, the field water holding capacity is above 80%, the cucumber is higher, and the tomato is slightly lower, at the peak of the result. The soil moisture content should be higher, reaching more than 90%.
7. Why can't the surface ploughed soil be used as the back wall soil when building a new greenhouse?
The economic benefits of greenhouse vegetables are better than those of open vegetables. Coupled with the support of national policies, many vegetable greenhouses have been added every year throughout the country. However, it is easy to have a problem at the beginning of the construction of the greenhouse. The engineering team that builds the greenhouse often excavates the original topsoil for use as a rear wall. As a result, the soil in the greenhouse was all a soil that had not grown plants.
The ploughed soil is formed by years of plant growth and cultivation management. The available NPK and medium and trace elements are high. The soil has many kinds of microorganisms and their quantity. It has good water permeability and is suitable for plant growth. These raw soils, which were originally in deep layers, are just the opposite. Plants grow, the things they want to eat are not good, the permeability of water and gas is poor, and the fertilizer applied to the soil is also difficult to convert into easy because of the small number of microorganisms. The form that is absorbed by the roots. After the vegetable is finally planted, it is difficult to grow new roots due to poor living environment, and there are a series of problems such as slow plant growth and yellow leaves. Therefore, when constructing a new vegetable greenhouse, it is necessary to supervise the construction team and move the surface soil to the side of the greenhouse first. After the construction of the greenhouse is completed, the mature soil will be moved back to the greenhouse.
8. Why do vegetables need to apply base fertilizer?
In the process of growth, it is necessary to absorb various nutrients, including large and medium-sized mineral nutrients such as NPK, calcium, magnesium, sulphur, zinc, iron and boron. People eat it in a single bite. Like three meals a day, vegetables grow with the growth of roots. Absorbs the nutrients in the soil, absorbs less at the seedling stage, and needs more after flowering, and decreases when it is close to maturity. The soil, in fact, is equivalent to the warehouse where the plants need nutrients. Therefore, before the rotary tillage, a larger amount of fertilizer should be applied according to the characteristics of the fertilizer required by the vegetables and the soil conditions. These fertilizers, after the soil is rotated, will be in the deeper soil, so it is called the base fertilizer, because it will supply the nutrients and absorption of vegetables throughout the growing season, so it is also called the base fertilizer.
Another major benefit of applying base fertilizer is that vegetable root growth has the habit of growing to the fat. Applying the fertilizer to the deep soil will “tempt†the vegetable roots to “work hard†to reach the deep soil and form a stronger root system. The ground part will grow better and more robust. It should be noted that after the rotary tillage, the fertilizer applied at the point of application before planting or planting, mainly supplies the nutrient absorption of the vegetable seedling stage, and does not belong to the base fertilizer, it is called the seed fertilizer. In general, the amount of base fertilizer applied is large, and the amount of fertilizer used is small.
9. Why do you have to apply fully decomposed farmyard manure?
As we all know, organic fertilizer, also known as farmyard manure, is one of the essential fertilizers for vegetable growth. However, the "body" of farmyard manure is too large, the roots of the roots are too small to absorb nutrients, and the roots of plants cannot directly absorb farmyard manure. The farmyard manure applied to the soil first becomes the deliciousness of various microorganisms in the soil, which is shared by them and eventually decomposed into various things of different sizes, some of which can be directly absorbed by the roots, and some stimulate the roots. Or microbes in the soil, the roots and microbial activities are strengthened, the roots grow better and stronger, and the nutrients in the soil are more smoothly transformed. However, not all of these decomposed things are beneficial to vegetable roots and soil microbes. Some are toxic. For example, the smell of chicken manure, cattle and sheep, pig manure, etc., not only people feel uncomfortable after smelling, the root system is also unbearable. After a long time, the roots will stop growing and rot. These poisonous gases that are volatilized from the soil will even directly damage the stems and leaves of the vegetable seedlings and appear to burn. With the application of unfertilized farmyard manure year after year, a large amount of harmful substances accumulate in the soil year by year, the soil properties are deteriorating, the number of beneficial microbial populations is reduced, and harmful organisms are gradually increasing, leading to root rot, blight, yellow Diseases such as wilting, nematodes, and root mites are increasing year by year, and it is impossible to prevent them. Therefore, the farmyard manure should be fermented and fermented in advance, and in the process of fermentation and decomposition, the harmful things are removed, leaving useful things and then applied to the soil.
10. Why are many farmers not willing to fertilize farmyard manure in advance?
In fact, many people know the need to apply fully decomposed farmyard manure, but most vegetable farmers are reluctant to ferment the farmyard manure first. There are two reasons. One is that it is too laborious to ferment and decompose, and the other is the feeling of luck and make-up. Therefore, there are two ways to solve this problem. One is to buy the commercial type of decomposed organic fertilizer directly, and the other is to find a more convenient way to ferment and decompose. Farmers prefer to spend money on fertilizers, but they are unwilling to buy organic fertilizer for two reasons. One is that they don't know what kind of organic fertilizer to buy, and the other is that the cost of buying commercial organic fertilizer is too high.
Sealand is a trustworthy manufacturer of CNG Dispenser Mass Flow Meter, LNG Dispenser Mass Flow Meter, LPG Dispenser Mass Flow Meter, ATEX, CE & IECEx approved.
With its high accuracy, wide rangeability and reliable performance, Sealand meter has been applied in many kinds of industries during the last 8 years. Unlike others who only focus on the measurement of liquid at normal pressure & temperature, Sealand has conquered the difficulty in the measurement under severe conditions, such as high pressure, high viscosity, high & low temperature.
Take CNG (compressed natural gas) for example. As the saying goes, the meter can measure anything else if it can measure CNG. It is quite hard to measure gas under high pressure. The sensor must be able to bear high pressure; in this way, the thickness of flow tube must be increased, so the transmitter shall be more sensitive to detect the signal; however, Sealand made it. Sealand's first model is specially designed for CNG dispenser, and now thousands of this model are put into use on the market.
Here are the pictures of Sealand Mass Flow Meter in Dispenser for your reference.
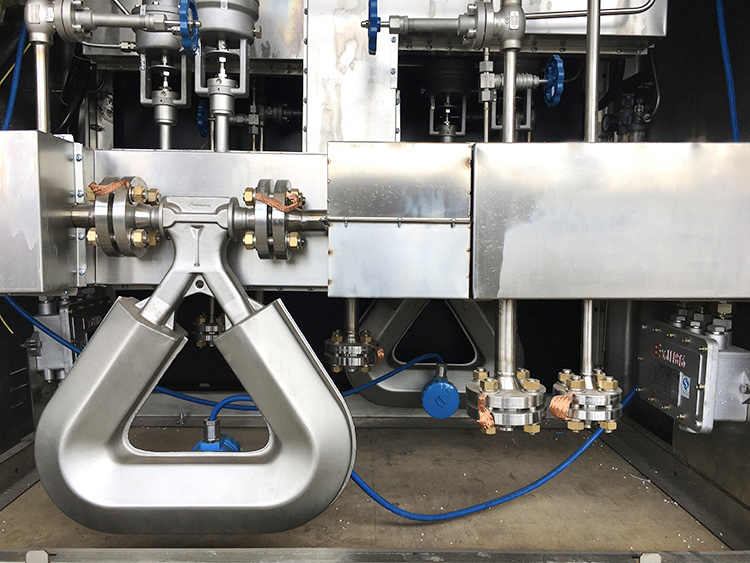
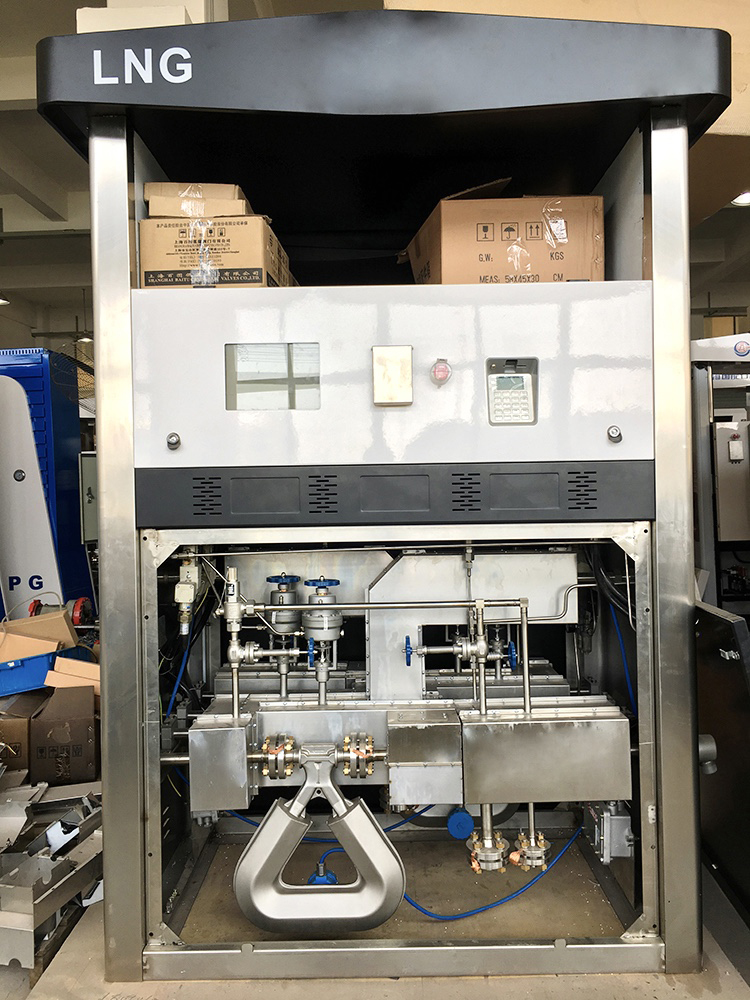
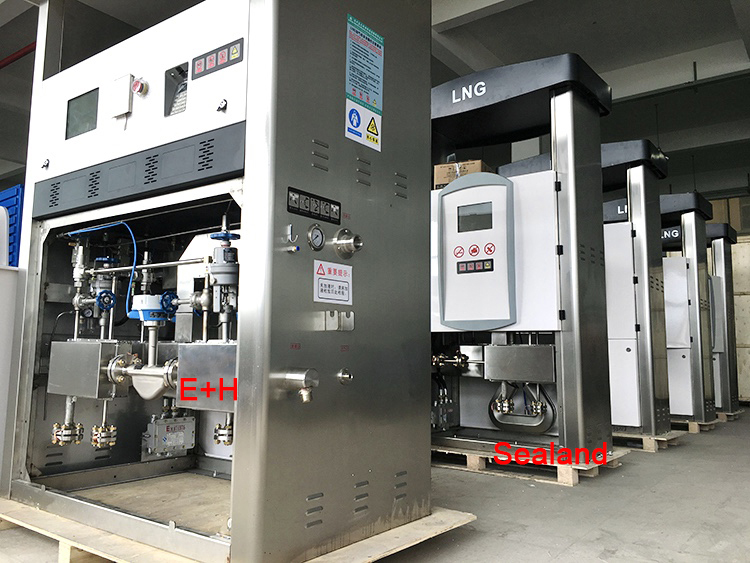
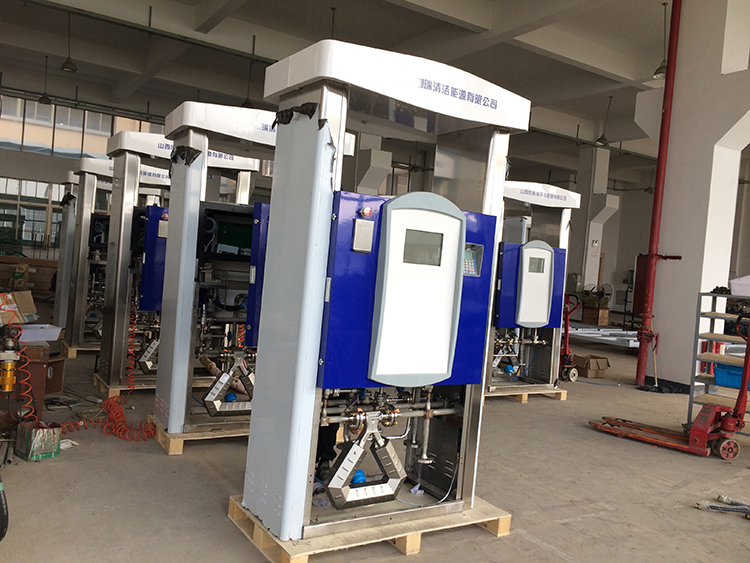
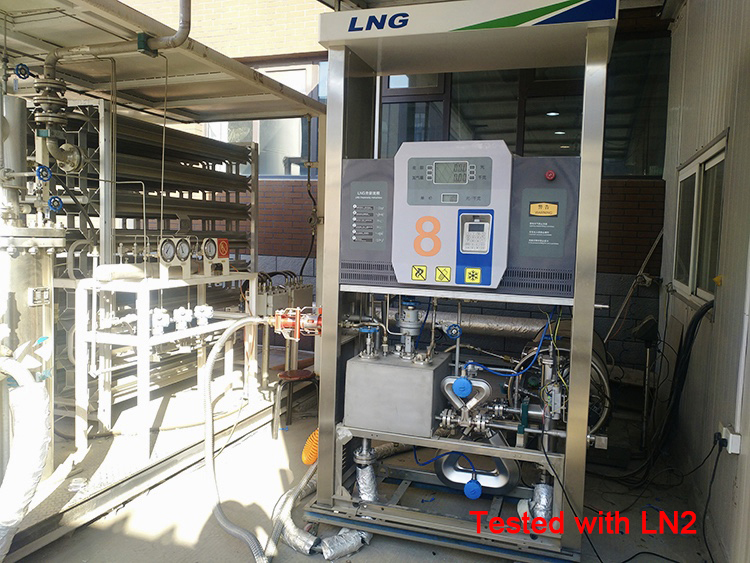
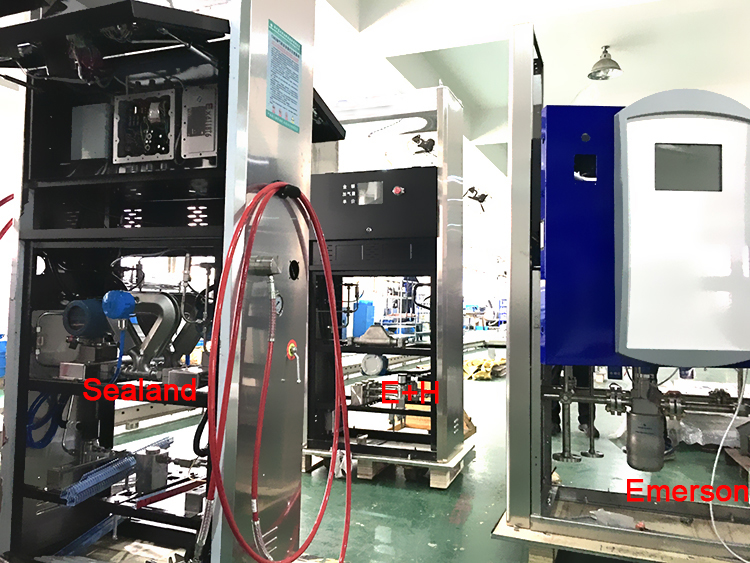
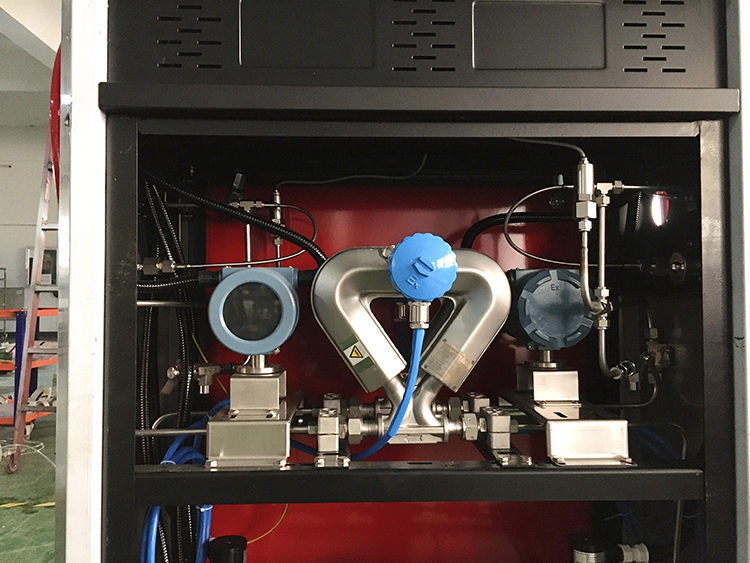
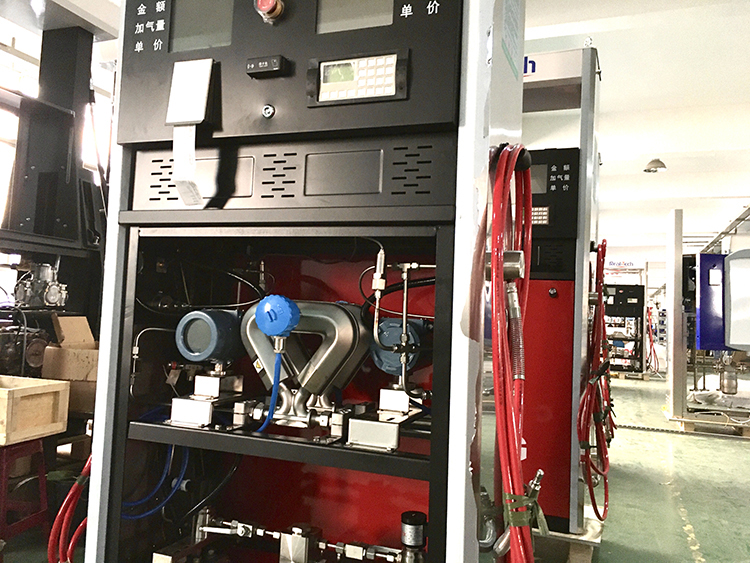
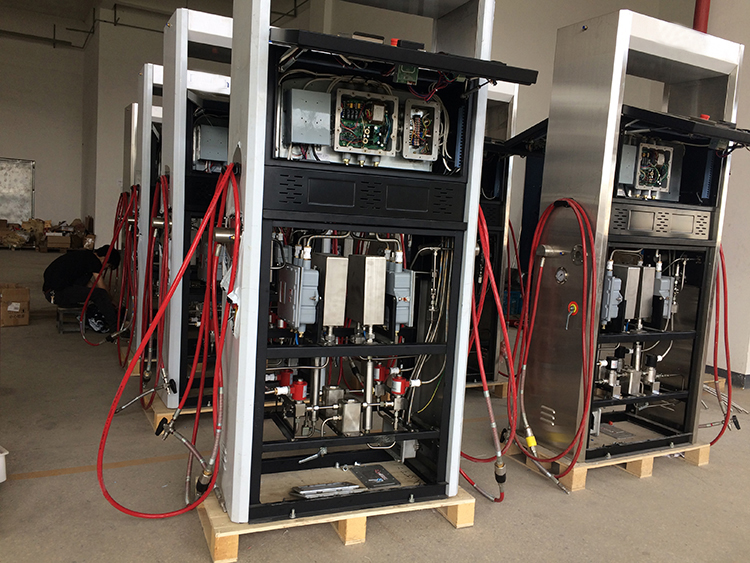
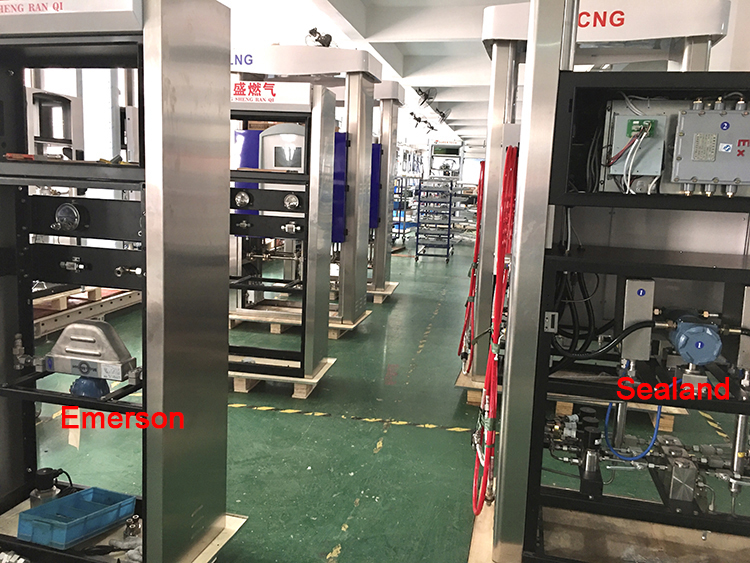











CNG Dispenser Mass Flow Meter, LNG Dispenser Mass Flow Meter, LPG Dispenser Mass Flow Meter
Zhejiang Sealand Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.sealandflowmeters.com